June 1, 2009
Circuit noise problems can originate from a variety of sources. By carefully examining attributes of the offending noise you can identify it’s source, thereby making noise reduction solutions become more apparent. There are three subcategories of noise problems: device, conducted and radiated noise. If an active or passive device is the major noise contributor, you […]
June 1, 2009
New separation kernels and embedded hypervisors can help ease the pain of migrating legacy systems to new hardware platforms, including multicore processing systems. Bringing multiple OSs and applications on to the same hardware also opens up new possibilities for combining systems that offer real-time performance within a familiar GUI environment. The LynxSecure separation kernel and […]
May 11, 2009
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a connectivity specification that provides ease-of-use, expandability and good performance for the end-user. It is one of the most successful interconnects in computer history. Originally released in 1995 for PCs, it now is expanding into use by embedded systems and is replacing older interfaces such as serial and parallel interfaces […]
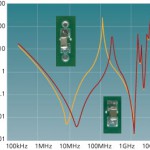
May 1, 2009
You must find, fix and design out signal integrity problems before committing to hardware. Simulation is the key.
May 1, 2009
Welcome to EDA Tech Forum’s low-power edition. Beginning with last year’s special focusing on PCBs, we began to take these occasional steps sideways from a broad-based agenda to concentrate on particularly active slices of the design world. Low-power has been a ‘hot button’ for some time, and the market originally fueled its importance. Cell phones […]
Article | Tags:
May 1, 2009
Traditional verification tools struggle to deal with today’s increasingly sophisticated power management technologies. One major limitation is that they cannot deal with varying power states because they make a built-in assumption that devices are always fully powered on. Further, power-aware verification at the register-transfer level is proving increasingly problematic, although it is also becoming increasingly […]
May 1, 2009
Since 130nm, you have either had an innovative approach to low-power design, or you have not had a business. From that node onwards, low-power requirements began to match raw performance in driving the R&D agenda. Where the cutting edge was once defined by communications infrastructure and programmable logic, consumer electronics (CE) started to become ever […]
May 1, 2009
The article describes the context and need for embedded operating systems that are more responsive to the power management demands placed on today’s electronic devices. It reviews the design objectives for the two main types of power management, reactive and proactive, and examines how both can be implemented. For decades, scientists and engineers have been […]
May 1, 2009
The article describes a dedicated low-power functional verification methodology, originally developed at STMicroelectronics (now ST-Ericsson). The article details the content, sequence and effectiveness of the methodology as it was tested on a 45nm system-on-chip design. In order of use, the main components are: A high-level verification language testbench Formal verification Rule checking C function library […]
May 1, 2009
The architectures that underpin today’s traditional place-and-route tools are showing their age, largely because their static timing analysis engines cannot handle more than two mode/corner scenarios. Thus limited, the software struggles to effectively implement low-power design techniques beyond such established concepts as clock gating and multiple threshold voltages. Designers run into difficulties when trying to […]