Cortus adds Arduino interface to SoC development board
Processor IP company Cortus has created a development board for its APS processor cores that includes a physical interface to Arduino Due shields, the add-on boards for the Arduino microcomputer. The move should make it easier to build prototypes for embedded applications such as smartcards, video processing, sensors, touchscreen controllers, wireless, security, industrial control and the Internet of Things (IoT).
“Developing drivers, porting software and validating the hardware/software interface is one of the key time-to-market challenges of developing SoCs with embedded processors,” said Christopher Kopetzky, vice president of engineering at Cortus. “The new platform combines Cortus’ proven software development tools with the ability to extend the board through Arduino Due-compatible shields and DDR2 memory.”
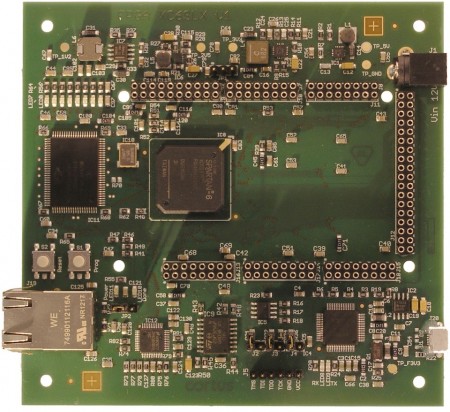
Figure 1 Cortus development board with Arduino Due shield interface (Source: Cortus)
The Cortus Development Platform board includes a Xilinx Spartan-6X75, 1Mbyte of synchronous SRAM for configuration and application software, and 32Mbit of serial flash. A 10/100 Mbits/s Ethernet transceiver PHY is connected to the FPGA and compatible with the Cortus 10/100 Ethernet MAC IP block. JTAG is provided through a USB interface. Additional I/O connectors enable the DDR2 memory to be up to 512Mbyte.
The capacity of the Spartan-6 X75 means that emulating a Cortus APS23 core will take up the 19% of the FPGA’s logic and the APS25, 29%. This means that it should be possible to emulate multicore systems on a single dev board. Extending the memory makes it possible to include a USB 2.0 PHY and a Cortus USB 2.0 controller in order to create a prototyping platform for embedded Linux systems.
The Development Platform also includes the Cortus Eclipse IDE and Cortus GCC toolchain, although other tool chains can be used. The Cortus 32bit processor IP cores are designed for embedded processing applications coded in C or C++.